Chemistry
Inviting Applications for PMRF- Prime Minister Research Fellows
Welcome to the Department of Chemistry at IIT Patna.
The Department of Chemistry in IIT Patna has been established since the setting up of the Institute in 2008. The department started the PhD program in Chemistry from July 2009. A vibrant multidisciplinary research program in the Department of Chemistry at IIT Patna is supported by energetic faculty members and state-of-the-art research facilities. The faculty members of the department are committed to quality teaching and research. With a strong foundation in the conventional areas and quest for emerging areas of Chemistry, faculty and students are engaged in a range of dynamic research programs that include Supramolecular Chemistry, Target and Diversity oriented Organic synthesis, Nanochemistry, Catalysis, high resolution and Bio-Spectroscopy, Polymer and Biochemistry.
“Applicants having valid CSIR-NET(JRF)/UGC-NET(JRF)/DST-INSPIRE /DBT/any other fellowship from recognized government funding agencies may apply for Ph.D. at anytime.”
Seema Singh, Manoj K. Singh and Prolay Das*
Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical doi.10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.100
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925400517315228)
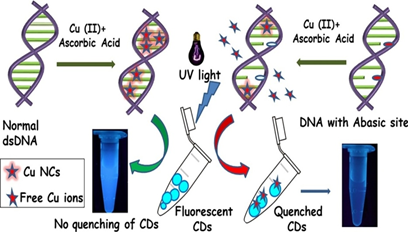
Biosensing of solitary and clustered a basic site DNA damage lesions with copper nanoclusters and carbon dots.
An easy, cost effective and visually detectable method for biosensing of abasic site damaged lesion in DNA by using copper nanoclusters (Cu NCs) and carbon dots (CDs) as fluorescent probes. Presence of abasic sites in DNA visually detected in presence of only UV light without any instruments. Accumulation of abasic sites lesions in DNA often considered as stress induced biomarker for radiation exposure,carcinogenesis,chromosomal abnormalities, mutations, aging related diseases and metastasis. Thus, detecting abasic sites in DNA is crucial for diagnosis of many diseases including cancer.
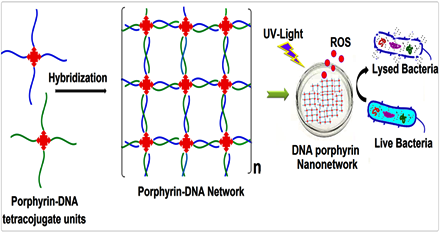
Self-assembly of DNA-porphyrin hybrid molecules for the creation of antimicrobial nanonetwork.
The construction of novel self-assembled DNA-porphyrin hybrid nanonetworks that utilize the porphyrin core for antibacterial applications. Porphyrin derivative with four pendant NH2 groups was synthesized and conjugated with the 5′-PO4 of ss-DNA by solution phase phosphoramidation coupling reaction. The conjugation was followed by DNA hybridization mediated self-assembly to form DNA-porphyrin hybrid nanonetwork. The enhanced antimicrobial property of the nanonetwork was envisioned following light irradiation at relevant wavelength.
Rina Kumari, Mohd. Imran Khan, Sourav Bhowmick, Kislay K. Sinha,
Neeladri Das* and Prolay Das*
Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology, B: Biology, 172 (2017), 28-35
Seema Singh, Anshul Mishra, Rina Kumari, Kislay K. Sinha, Manoj K.
Singh and Prolay Das
Carbon 114 (2017) 169-176
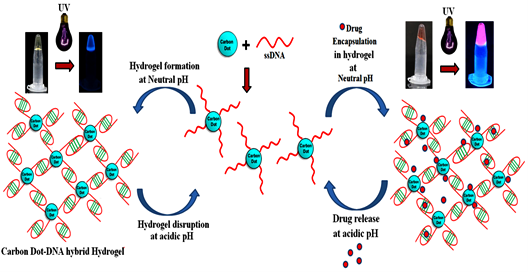
Carbon Dots Assisted Formation of DNA Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Drug
The construction of DNA-carbon dot (CD) hybrid hydrogel for targeted and sustained release of drug molecules is reported here. Amine functionalized carbon dots were conjugated to 5’-phosphate termini of Cytosine (C) rich ssDNA by phosphoramidate linkage. As a prototype, chemotherapeutic drug Doxorubicin (Dox) was loaded and enclosed in hydrogel that acts as a container for sustained release of the drug.
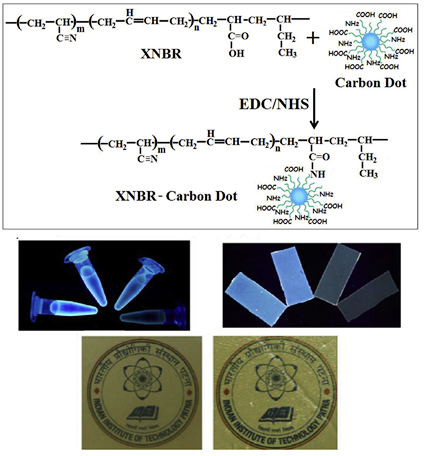
Carbon dot e Unique reinforcing filler for polymer with special reference to physico-mechanical properties.
This work reports the reinforcing efficiency of carbon dots (CDs) in carboxylated acrylonitrile butadiene (XNBR) latex at very low concentration. Amine and carboxyl functionalized CDs have been synthesized from citric acid and glycine. The CDs are covalently conjugated to XNBR latex using 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC.HCl) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) as coupling agents. This is the first report which analyzes the effect of CDs on the physico-mechanical properties of elastomer contrary to the other novel fillers of carbon family.
P.R. Sreenath, Seema Singh, M.S. Satyanarayana, Prolay Das, K. Dinesh
Kumar
Polymer 112 (2017) 189-200
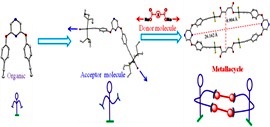
Jana, A.; Das, N. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 4099–4105.
Self-Assembly of [2+2] Platina Macrocycles Using a Flexible Organometallic Clip.
A new pyrazine-based ditopic Pt(II) organometallic clip has been designed that is “flexible” due to presence of ether functional groups bridging the core (pyrazine) and periphery(PtIIunits).Itself-assembles with dicarboxylates to yield nanoscalar metallacycles.
Pyrazine based Pt(II) bis-alkynyl organometallic complexes: synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxic effect on A549 human lung carcinoma cells
Five new pyrazine-based organometallic complexes containing a pyrazine ring in the center and have two Pt(II)-alkynyl branches protruding on either side have been synthesized. These pyrazine-containing and π-conjugated Pt(II)-alkynyl complexes are quite rare. For the first time, these organometallic complexes have shown a potential application: cytotoxic potency against A549 human lung carcinoma cells.
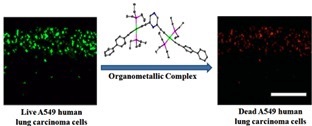
Bhowmick, S.; Jana, A. Marri, S. R.; Gupta, P.; Behera, J. N.; Mandal, B. B.
Das, N. App. Org. Chem., DOI: 10.1002/aoc.3824
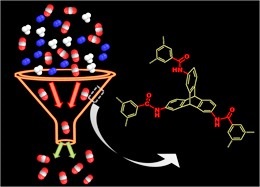
Bera, R.; Mondal, S.; Das, N. Polymer 2017, 111, 275-284.
Nanoporous triptycene based network polyamides (TBPs) forselective CO2uptake
Facile syntheses of triptycene based polyamide networks (TBPs).TBPs are thermally stable, porous and exhibit reasonably high surface area (upto 80 m2 g−1). The CO2uptake (upto 1.38 mmol/g at 273 K and 1 bar) and CO2/N2 selectivity ( upto 60 at 298 K) of these TBPs are noteworthy.
Theoretical studies on gas-phase kinetics and mechanism of H-abstraction reaction from methanol by ClO and BrO radicals.
The structural features, spectroscopic properties, and interaction energies of the linear proton-bound complexes of OCH+ and its sulfur analog SCH+ with N2 were investigated using the high-level ab initio methods MP2 and CCSD(T) as well as density functional theory with the aug-cc-pVXZ (X = D, T) basis sets. A theoretical investigation of the energetics and spectroscopic properties of the gas-phase linear proton-bound cation–molecule complexes, "XCH+ –N2 (X = O, S).
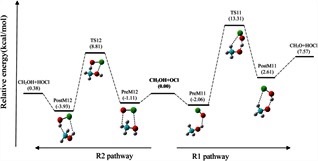
S. Begum, R. Subramanian, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 39110–39121
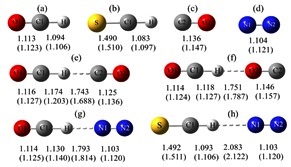
S. Begum, R. Subramanian, J. Mol. Model, 2016,22:6
A theoretical investigation of the energetics and spectroscopic properties of the gas-phase linear proton-bound cation–molecule complexes, XCH–N2 (X = O, S)
The structural features, spectroscopic properties, and interaction energies of the linear proton-bound complexes of OCH+ and its sulfur analog SCH+ with N2 were investigated using the high-level ab initio methods MP2 and CCSD(T) as well as density functional theory with the aug-cc-pVXZ (X = D, T) basis sets.
Copper (II)-Mediated Aerobic Oxidation of Benzylimidates: Synthesis of Primary α-Ketoamides
A simple and straightforward method for the synthesis of primary α-ketoamides has been discovered. The reaction represents the first example of benzylimidates directly converting in to primary α-ketoamides by using sustainable molecular oxygen as an oxidant.
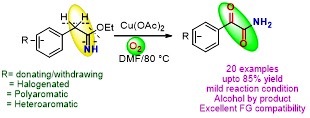
Y. Kumar, M. Shaw, R. Thakur, A. Kumar J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 6617−6625
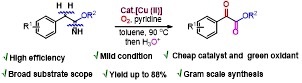
Y. Kumar, Y. Jaiswal, A. Kumar J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 12247−12257
Copper(II)-Catalyzed Benzylic C(sp3)-H Aerobic Oxidation of (Hetero)Aryl Acetimidates: Synthesis of Aryl α-Ketoesters
A straightforward method is developed in this paper for the synthesis of α-ketoesters through copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of (hetero)aryl acetimidates using molecular oxygen as a sustainable oxidant. The reaction represents the first example of the direct synthesis of α-ketoesters from arylacetimidates through the aerobic oxidation of a benzylic C(sp3)−H (C=O) bond in moderate to good yield.
Primary Amide Directed Regioselective ortho-C−H-Arylation of (Aryl)Acetamides
An efficient and regioselective palladium (II)-catalyzed primary acetamide assisted ortho arylation of arylacetamide has been discovered. This is the first report where functionalizable primary acetamide (−CH2CONH2) is used as a directing group for C(sp2)−H activation/crosscoupling reactions, circumventing the extra steps of installation and subsequent removal of the directing groups.
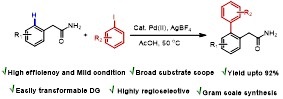
Y. Kumar, Y. Jaiswal, A. Kumar J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 12499−12505
.